IP (Internet Protocol)
- For routing of packets and Quality of Service (giving some packets preferential treatment)
- It is a connectionless protocol with no acknowledgments at Layer 3
- Logical addressing via IPv4 and IPv6; dividing the network (subnetting) provides better performance, security, and makes troubleshooting easier
- Layer 2 uses MAC addresses that are one big flat addressing scheme
- Types of traffic are Unicast, Broadcast, and Multicast
IP Addressing Formate
- Binary counting with (4) 8 bit, dotted decimal octets = 32 bits total
- ex 192.168.10.15 = 11000000.10101000.00001010.00001111
- The Subnet Mast defines what portion of the IP Address is the network address (all 1s) and what portion is the host address (all 0s)
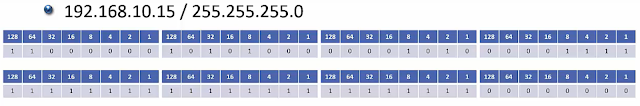
- All 0's in the host portion designate the network address, and can not be assigned to a host. ex 192.168.10.0
- All 1's in the host portion designate the broadcast address of the subnet, and traffic with this destination address will be sent to all hosts in the subnet. 192.168.10.255; this address can not be assigned to a host
- Subnet Mast in Slash Notation above would be 192.168.10.15 /24 for the host, and 192.168.10.0 /24 for the Network Address


No comments:
Post a Comment