- DHCP is a client/server protocol that automatically provides a host with an IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
- Can assign additional IP configuration values by means of DHCP options like the TFTP address for phones to find the phone system
- DHCP relay agent can forward initial DHCP messages throughout the campus so a server is not needed on every network or subnet
- Candidates are PCs and laptops, not servers or network infrastructure.
- UDP port number 67 for the DHCP server, and the UDP port number 68 for the client.
Option 1: Cisco DHCP Server Configuration
- R1(config)#ip dhcp exclude-address 10.10.10.1 10.10.10.10 (enter this first so these addresses are not assigned by turning dhcp on)
- R1(config)#ip dhcp pool 10.10.10.0_Clients (any name can be assigned)
- R1(dhcp-config)# network 10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0 (network to be handed out)
- R1(dhcp-config)# default-router 10.10.10.1
- R1(dhcp-config)# dns-server 10.10.20.10
- Verification
- Show ip dhcp pool
- Show ip dhcp binding (shows assigned IP addess to MAC address)
Option 2: External DHCP Server Configuration
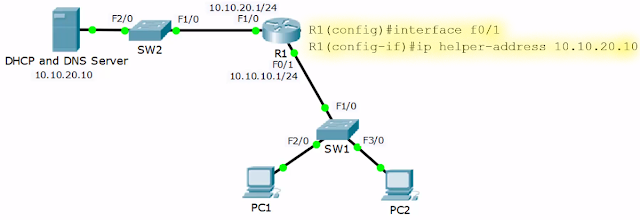
- If the DHCP server is on a different subnet, the Router interface facing the clients need not block the DHCP request broadcast traffic, but to help it through the network
- R1(config)#interface fa0/1
- R1(config-if)# ip helper-address 10.10.20.10
Option 3: Cisco Router as DHCP Client
- Example: if router interface connects to an ISP and there is on need for a static internet address
- R1(config)# interface gi0/0
- R1(config-if)# ip address dhcp
- R1(config-if)# no shutdown
- Verification
- show dhcp lease


No comments:
Post a Comment